
Setting up a Graylog server is a simple process, requiring a MongoDB database and an Elasticsearch database to support it.

One of the more popular choice is Graylog. There are many logging solutions available in the open source world. So a logging system built for Distributed Computing would be most ideal to use here. Without this, it would be very difficult to diagnose any problem by trying to piece together logs from multiple sources. In a Distributed Architecture, one of the main components that needs to be created is a robust Logging System.
PWGEN CENTOS 8 INSTALL
For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Graylog website.In this article, I will take you through the steps to Install Graylog on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Graylog in CentOS 8 system.
PWGEN CENTOS 8 PASSWORD
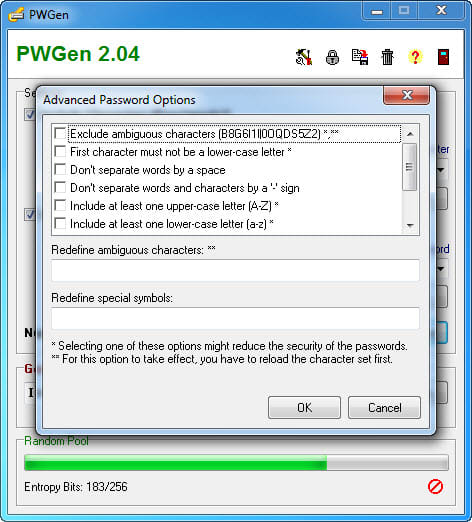
Log in with username admin and the password you configured at root_password_sha2 on nf.Ĭongratulations! You have successfully installed Graylog. Open your favorite browser and navigate to or and complete the required steps to finish the installation. Graylog will be available on HTTP port 9000 by default. Http_external_uri = After you have modified the configuration file, restart the Graylog service: sudo systemctl daemon-reload Root_password_sha2 = e7cf3ef4f17c3999a94f2c6f612e8a888e5b10268bmwe4619398b23bd38ec221aĮnable the Graylog web interface by editing the nf file: nano /etc/graylog/server/nf http_bind_address = your-server-ip:9000 Make changes to the file as shown below: password_secret = 1dcw10Snsvk1bKgkARGNaalO3QeZqkPG8pUcbJO3oFmeilanamariarFixOR95Nrv40FCFRClXIdnxwknGtl4HDrTspWmom Then, edit the nf file to begin the Graylog configuration: nano /etc/graylog/server/nf Next, create a hash password for the root user that can be used to log in to the Graylog web server using the following command: echo -n yourpassword | shasum -a 256 Results: 1dcw10Snsvk1bKgkARGNaalO3QeZqkPG8pUcbJO3oFmeilanamariarFixOR95Nrv40FCFRClXIdnxwknGtl4HDrTspWmom Install Graylog server using dnf: sudo dnf install graylog-serverĪfter you have installed the Graylog Server, you have to generate a secret key for Graylog using the following command: pwgen -N 1 -s 96 Now install the Graylog repository configuration: sudo dnf install Start the MongoDB service and enable it to start on boot with the following command: sudo systemctl enable rvice Install MongoDB by running the following command: sudo dnf install mongodb-org You will need to add the MongoDB repo first:Ĭat /etc//mongodb-org-4.0.repo MongoDB is not available in the default CentOS repository. Reload the systemctl daemon and enable Elasticsearch to start automatically on the system startup: sudo systemctl daemon-reloadĬheck the health of the Elasticsearch with the following command: curl -X GET Step 5. You need to modify the Elasticsearch configuration file and set the cluster name to Graylog: nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlĬhange the file as shown below: cluster.name: graylog Then, install Elasticsearch using the following command: sudo dnf install elasticsearch-os Name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages Now, we Add Elasticsearch repository: cat /etc//elasticsearch.repo So, install either OpenJDK or Oracle JDK using the following command: sudo dnf install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headlessĬheck if it is successfully installed: java -versionįirst, import the GPG signing key before the installation: rpm -import
Sudo dnf install wget pwgen perl-Digest-SHĮlasticsearch requires Java to be installed on the system. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date. We recommend acting as a non-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
